Gritty Practical Leadership Book Five Star Review Try It on Amazon
Real Leadership Without the Gloss — Lessons That Last –Book Review Introduction Most leadership books fall into one of
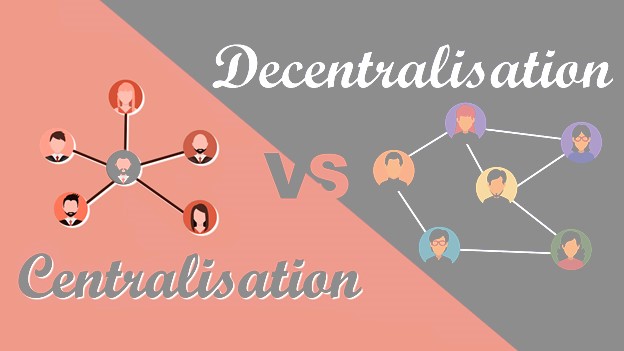
Decentralizing authority has become a fundamental tactic in today’s business environment for developing an empowered and proactive staff. The transition from a strict hierarchical framework to a more flexible and collaborative model is a crucial step in improving overall performance, creativity, and organizational dynamism. Organizations may foster a workforce that is more capable, engaged, and responsive by decentralizing authority. This paper explores the subtleties of decentralizing authority, providing a thorough analysis and advanced vocabulary to explain its benefits, methods, and implementation difficulties.
Redistributing decision-making authority from higher organizational levels to lower ones is known as decentralizing authority. This structural reorganization increases the organization’s responsiveness and strategic agility while also democratizing decision-making. Businesses can tap into a wider range of insights, expedite problem-solving procedures, and improve overall operational efficiency by giving employees more autonomy. Decentralization’s fundamental tenet is the development of a workforce culture characterized by intrinsic motivation, trust, and accountability.
One of the main components of decentralizing authority is delegation. It is assigning particular decision-making authority and duties to workers at different levels of the hierarchy. The right amount of autonomy and supervision must be balanced for effective delegation. Managers need to provide clear guidelines for staff to work independently within while also providing systems for assistance and direction. By delegating decision-making authority, this strategy distributes managerial resources while also enabling staff members to assume responsibility for their jobs.
Decentralization is best exemplified by participatory management or participatory decision-making. This strategy involves including staff members in the creation and implementation of strategic choices. Organizations can leverage collective intelligence and promote a more inclusive decision-making process by requesting input and feedback from a broad range of personnel. By incorporating a variety of viewpoints, participatory management improves decision-making and increases employee engagement by exhibiting organizational respect for their contributions.
A strong foundation for empowerment must be established for decentralization of authority to be successful. These frameworks include guidelines, protocols, and methods intended to support and control the transfer of power. Good empowerment frameworks should include accountability and feedback mechanisms, as well as explicit roles and responsibilities and standards for decision-making. These kinds of frameworks guarantee that the decentralization process is equitable, logical, and consistent with organizational goals.
The effectiveness of decentralized authority is heavily dependent on how ready staff members are to take on more responsibility. Employees must participate in extensive training and development programs in order to acquire the necessary knowledge and abilities. These courses ought to emphasize skills like problem-solving, strategic thinking, and leadership. By making an investment in ongoing professional growth,
Successful decentralization of authority depends critically on effective communication. To make sure that workers are informed and in line with company objectives, organizations need to set up clear and effective communication channels. Information flow and an open culture can be promoted by frequent updates, feedback channels, and cooperative platforms. Improved channels of communication foster cohesion and confidence among employees while also aiding in the decentralization process.
Resistance to change is one of the main issues with decentralizing authority. Workers who are used to conventional hierarchical arrangements could be reluctant to switch to a more decentralized method. Organizations should use change management techniques that prioritize employee involvement, transparent communication, and progressive adoption in order to lessen resistance. Incorporating workers into the process of change and showcasing the advantages of decentralization can mitigate opposition and promote a more seamless shift.
To prevent suspicions of unfairness or partiality, decentralized authority must be applied consistently. Standardized protocols and rules for delegating authority and making decisions must be established and upheld by organizations. These procedures may be effectively monitored and evaluated on a regular basis to make sure they are in line with organizational values. Maintaining consistency in the implementation process not only upholds equity but also preserves the integrity of the decentralization process.
Decentralized authority can be rendered ineffective by inadequate training. Workers who are not equipped with the right information or abilities may find it difficult to carry out their jobs well, which could result in mistakes or inefficiencies. Organizations should make investments in thorough, continuous training programs that fill in recognized skill gaps in order to handle this challenge. Targeted resources and assistance can improve workers’ capacity and preparedness, which will help decentralization’s overall success.
One game-changing tactic for developing an empowered and engaged workforce is decentralizing authority. Organizations can improve operational efficiency, innovation, and employee satisfaction by putting strategies like robust empowerment frameworks, participative management, and delegation of decision-making authority into practice. Strategic planning and efficient management can help to mitigate problems like training gaps and resistance to change. In the end, decentralizing authority promotes persistent competitive advantage in the dynamic corporate environment while also revitalizing organizational dynamics. By using these strategies wisely, businesses can develop a staff that is more flexible, adaptable, and driven, setting them up for long-term success and expansion.
Real Leadership Without the Gloss — Lessons That Last –Book Review Introduction Most leadership books fall into one of
A Masterclass in Leadership Through Real Stories Leadership Stories from the Corporate Jungle and Navy Deck Plates: Real Lessons,
Dr. Tom DePaoli CEO Apollo Solutions won an award for his book “Leadership by Storytelling: The Best Way to Learn Good Leadership Skills”,
Copyright © 2024 Dr. Tom’s Advice Blog | Powered by Dr. Tom’s Advice Blog